56 * 5.8[1] 324.8Workshop: Dealing with Data in R
steffilazerte
@steffilazerte@fosstodon.org
@steffilazerte
steffilazerte.ca

Compiled: 2026-02-19




A programming language is a way to give instructions in order to get a computer to do something
R, what is 56 times 5.8?
(I made these slides with a mix of R and Quarto)


David Whittaker
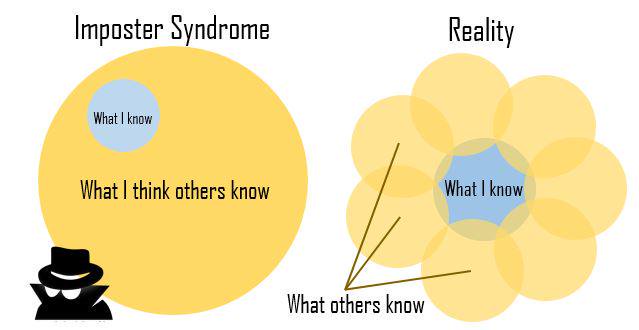
Moral of the story?
Make friends, code in groups, learn together and don’t beat yourself up

Artwork by @allison_horst

Let’s setup a project in RStudio!
Let’s change some options in RStudio!
Open New File
(make sure you’re in the RStudio Project)
Write library(tidyverse) at the top
Save this new script
(consider names like intro.R or 1_getting_started.R)
Ctrl-Enter# First load the packages
library(palmerpenguins)
library(ggplot2)
# Now create the figure
ggplot(data = penguins, aes(x = body_mass_g, y = bill_length_mm, colour = species)) +
geom_point()Warning: Removed 2 rows containing missing values or values outside the scale range
(`geom_point()`).# First load the packages
library(palmerpenguins)
library(ggplot2)
# Now create the figure
ggplot(data = penguins, aes(x = body_mass_g, y = bill_length_mm, colour = species)) +
geom_point()Warning: Removed 2 rows containing missing values or values outside the scale range
(`geom_point()`).Let’s talk about the parts of the code first
Later we’ll talk about why this works
# First load the packages
library(palmerpenguins)
library(ggplot2)
# Now create the figure
ggplot(data = penguins, aes(x = body_mass_g, y = bill_length_mm, colour = species)) +
geom_point()Warning: Removed 2 rows containing missing values or values outside the scale range
(`geom_point()`).Packagesggplot2 and palmerpenguins
# First load the packages
library(palmerpenguins)
library(ggplot2)
# Now create the figure
ggplot(data = penguins, aes(x = body_mass_g, y = bill_length_mm, colour = species)) +
geom_point()Warning: Removed 2 rows containing missing values or values outside the scale range
(`geom_point()`).Functionslibrary(), ggplot(), aes(), geom_point()
# First load the packages
library(palmerpenguins)
library(ggplot2)
# Now create the figure
ggplot(data = penguins, aes(x = body_mass_g, y = bill_length_mm, colour = species)) +
geom_point()Warning: Removed 2 rows containing missing values or values outside the scale range
(`geom_point()`).+
(Specific to ggplot)
# First load the packages
library(palmerpenguins)
library(ggplot2)
# Now create the figure
ggplot(data = penguins, aes(x = body_mass_g, y = bill_length_mm, colour = species)) +
geom_point()Warning: Removed 2 rows containing missing values or values outside the scale range
(`geom_point()`).Figure!
# First load the packages
library(palmerpenguins)
library(ggplot2)
# Now create the figure
ggplot(data = penguins, aes(x = body_mass_g, y = bill_length_mm, colour = species)) +
geom_point()Warning: Removed 2 rows containing missing values or values outside the scale range
(`geom_point()`).Warning
# First load the packages
library(palmerpenguins)
library(ggplot2)
# Now create the figure
ggplot(data = penguins, aes(x = body_mass_g, y = bill_length_mm, colour = species)) +
geom_point()Warning: Removed 2 rows containing missing values or values outside the scale range
(`geom_point()`).Comments
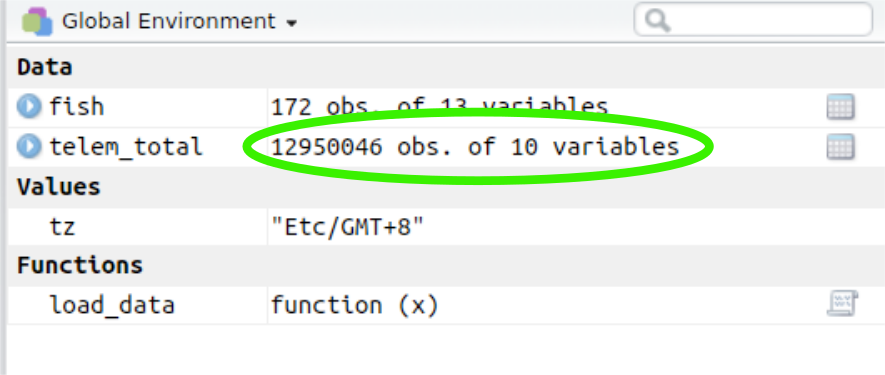
Objects are things in the environment
(Check out the Environment pane in RStudio)
e.g., library() - Loads an R package so we can use it’s functions and other objects it supplies
data, x, y, colourThis error states that we’ve assigned the argument trim to a non-valid argument
Where did trim come from?

vectors or data.frames (also tibbles)
mpg cyl disp hp drat wt qsec vs
Mazda RX4 21.0 6 160.0 110 3.90 2.620 16.46 0
Mazda RX4 Wag 21.0 6 160.0 110 3.90 2.875 17.02 0
Datsun 710 22.8 4 108.0 93 3.85 2.320 18.61 1
Hornet 4 Drive 21.4 6 258.0 110 3.08 3.215 19.44 1
Hornet Sportabout 18.7 8 360.0 175 3.15 3.440 17.02 0
Valiant 18.1 6 225.0 105 2.76 3.460 20.22 1
Duster 360 14.3 8 360.0 245 3.21 3.570 15.84 0
Merc 240D 24.4 4 146.7 62 3.69 3.190 20.00 1
Merc 230 22.8 4 140.8 95 3.92 3.150 22.90 1
Merc 280 19.2 6 167.6 123 3.92 3.440 18.30 1
Merc 280C 17.8 6 167.6 123 3.92 3.440 18.90 1
Merc 450SE 16.4 8 275.8 180 3.07 4.070 17.40 0
Merc 450SL 17.3 8 275.8 180 3.07 3.730 17.60 0
Merc 450SLC 15.2 8 275.8 180 3.07 3.780 18.00 0
Cadillac Fleetwood 10.4 8 472.0 205 2.93 5.250 17.98 0
Lincoln Continental 10.4 8 460.0 215 3.00 5.424 17.82 0
Chrysler Imperial 14.7 8 440.0 230 3.23 5.345 17.42 0
Fiat 128 32.4 4 78.7 66 4.08 2.200 19.47 1
Honda Civic 30.4 4 75.7 52 4.93 1.615 18.52 1
Toyota Corolla 33.9 4 71.1 65 4.22 1.835 19.90 1
Toyota Corona 21.5 4 120.1 97 3.70 2.465 20.01 1
Dodge Challenger 15.5 8 318.0 150 2.76 3.520 16.87 0
AMC Javelin 15.2 8 304.0 150 3.15 3.435 17.30 0
Camaro Z28 13.3 8 350.0 245 3.73 3.840 15.41 0
Pontiac Firebird 19.2 8 400.0 175 3.08 3.845 17.05 0
Fiat X1-9 27.3 4 79.0 66 4.08 1.935 18.90 1
Porsche 914-2 26.0 4 120.3 91 4.43 2.140 16.70 0
Lotus Europa 30.4 4 95.1 113 3.77 1.513 16.90 1
Ford Pantera L 15.8 8 351.0 264 4.22 3.170 14.50 0
Ferrari Dino 19.7 6 145.0 175 3.62 2.770 15.50 0
Maserati Bora 15.0 8 301.0 335 3.54 3.570 14.60 0
Volvo 142E 21.4 4 121.0 109 4.11 2.780 18.60 1
am gear carb
Mazda RX4 1 4 4
Mazda RX4 Wag 1 4 4
Datsun 710 1 4 1
Hornet 4 Drive 0 3 1
Hornet Sportabout 0 3 2
Valiant 0 3 1
Duster 360 0 3 4
Merc 240D 0 4 2
Merc 230 0 4 2
Merc 280 0 4 4
Merc 280C 0 4 4
Merc 450SE 0 3 3
Merc 450SL 0 3 3
Merc 450SLC 0 3 3
Cadillac Fleetwood 0 3 4
Lincoln Continental 0 3 4
Chrysler Imperial 0 3 4
Fiat 128 1 4 1
Honda Civic 1 4 2
Toyota Corolla 1 4 1
Toyota Corona 0 3 1
Dodge Challenger 0 3 2
AMC Javelin 0 3 2
Camaro Z28 0 3 4
Pontiac Firebird 0 3 2
Fiat X1-9 1 4 1
Porsche 914-2 1 5 2
Lotus Europa 1 5 2
Ford Pantera L 1 5 4
Ferrari Dino 1 5 6
Maserati Bora 1 5 8
Volvo 142E 1 4 2rows x columns
Try out the following code…
environment change (upper right panel)?
Vectors
Data frames
Try out the following code…
: do?c() do?
Vectors
[index] to access part of a vectorTry out the following code…
Vectors
Apple is not the same as apple)Artwork by @allison_horst
This is correct:
This is not correct:
>80% of learning R is learning to troubleshoot!
(But don’t)
<- to assign values to objects= to set function arguments== to determine equivalence (logical)()(), R spits out information on the function:() must be associated with a function (Well, almost always)
[] [1] "A" "B" "C" "D" "E" "F" "G" "H" "I" "J" "K" "L" "M" "N" "O" "P" "Q" "R" "S"
[20] "T" "U" "V" "W" "X" "Y" "Z"[1] "A"[1] "Z"[] have to be associated with an object that has dimensions (Always!)
is easier to read than
(But the same, coding-wise)
Hard to read
Easier to read
(But the same, coding-wise)
Artwork by @allison_horst