Error: 'weather.csv' does not exist in current working directory ('/home/steffi/Projects/Workshops/workshop-dealing-with-data').Workshop: Dealing with Data in R
Loading & Cleaning Data in R
I know the file exists, why doesn’t R?
steffilazerte
@steffilazerte@fosstodon.org
@steffilazerte
steffilazerte.ca

Compiled: 2026-02-19
First things first
Save previous script
Open New File
(make sure you’re in the RStudio Project)
Write library(tidyverse) at the top
Save this new script
(consider names like cleaning.R or 3_loading_and_cleaning.R)
Download the data we’ll use in this workshop
- Create a ‘data’ folder in your RStudio project
- In the “Files” pane click on the folder icon OR
- Navigate to your project folder via your computer’s file browser
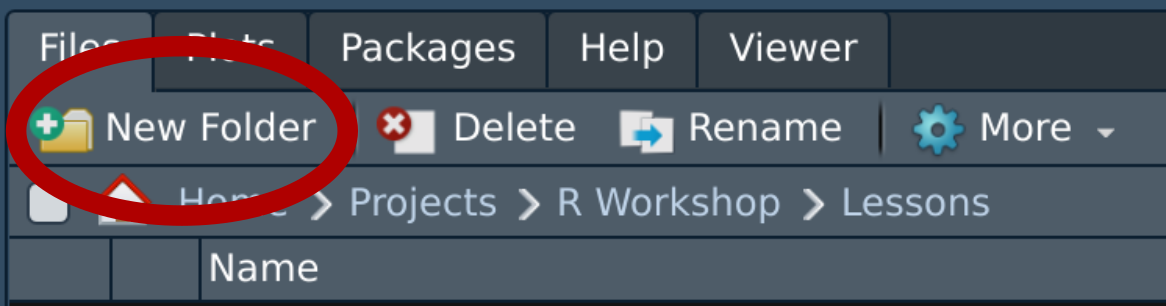
Click on “New Folder”
- Right-click “Save Link As..” and download these files to your data folder
Side Note
R base vs. tidyverse
R base vs. tidyverse
R base
- Basic R
- Packages are installed and loaded by default
- Base pipe
|>*

*We’ll cover pipes soon 😁
tidyverse
- Collection of ‘new’ packages developed by a team closely affiliated with RStudio
- e.g.,
ggplot2,dplyr,tidyr,readr - Packages designed to work well together
- e.g.,
- Use a slightly different syntax
- tidyverse pipe
%>%or base pipe|>*

Useful to know if functions aretidyverse or R base
Dealing with data
1. Loading data
- Get your data into R
2. Looking for problems
- Typos
- Incorrectly loaded data
3. Fixing problems
- Corrections
- Renaming
- Dealing with NA’s
4. Setting formats
- Text,
- Numbers
- Factors
- Dates
5. Saving your data
Loading Data
Data types: What kind of data do you have?
Specific program files
| Type | Extension | R Package | R function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Excel | .xls, .xlsx | readxl* |
read_excel() |
| Open Document | .ods | readODS |
read_ods() |
| SPSS | .sav, .zsav, .por | haven |
read_spss() |
| SAS | .sas7bdat | haven |
read_sas() |
| Stata | .dta | haven |
read_dta() |
| Database Files | .dbf | foreign |
read.dbf() |
Convenient but…
- Can be unreliable
- Can take longer
For files that don’t change, better to save as a *.csv
(Comma-separated-variables file)
 * part of the
* part of the tidyverse
Data types: What kind of data do you have?
General text files
| Type | R base | readr package * |
|---|---|---|
| Comma separated | read.csv() |
read_csv(), read_csv2() |
| Tab separated | read.delim() |
read_tsv() |
| Space separated | read.table() |
read_table() |
| Fixed-width | read.fwf() |
read_fwf() |
 * part of the
* part of the tidyverse
readrpackage especially useful for big data sets (fast!)- Error/warnings from
readrare a bit more helpful
We’ll focus on
readxlpackageread_excel()
readrpackageread_csv(),read_tsv()
Where is my data?
Common error
With no folder (just file name) R expects file to be in Working directory
Working directory is:
- Where your RStudio project is
- Your home directory (My Documents, etc.) [If not using RStudio Projects]
- Where you’ve set it (using
setwd()or RStudio’s Session > Set Working Directory)
Don’t use setwd()
Do use Projects in RStudio
Where is my data?
A note on file paths (file locations)
- folders separated by
/ homeis a folder
Where is my data?
A note on file paths (file locations)
- folders separated by
/ homeandsteffiare folderssteffiis a folder inside ofhome
Where is my data?
A note on file paths (file locations)
- folders separated by
/ home,steffi,Documents,R Projectsare folderssteffiis inside ofhome,Documentsis inside ofsteffi, etc.mydata.csvis a data file insideR Projectsfolder
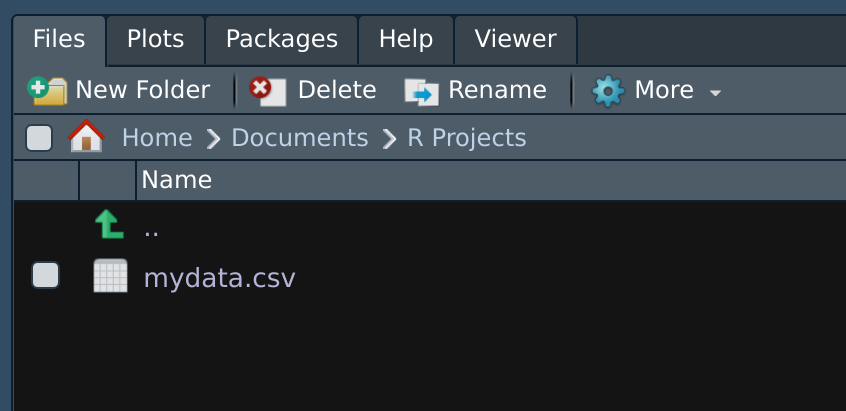
RStudio Files Pane
Where is my data?
Absolute Paths
| OS | Path |
|---|---|
| LINUX | /home/steffi/Documents/R Projects/mydata.csv |
| WINDOWS | C:/Users/steffi/My Documents/R Projects/mydata.csv |
| MAC | /users/steffi/Documents/R Projects/mydata.csv |
Full location, folders and filename
Relative Paths
| Path | Where to look |
|---|---|
| mydata.csv | Here (current directory) |
| ../mydata.csv | Go up one directory (../) |
| data/mydata.csv | Stay here, go into “data” folder (data/) |
| ../data/mydata.csv | Go up one directory (../), then into “data” folder (data/) |
Only relative info
Use relative symbols (e.g., ../)
With RStudio ‘Projects’ only need to use relative paths
Keep yourself organized
For simple projects
- Create an ‘RStudio Project’ for each Project
- Create a specific “data” folder within each project (one per project)
Let’s load some data!
A reminder about Assignments!
<-- “Assign” an object to a handle/name
my_figureis an R object, specifically a ggplot2 figuremy_datais an R object, specifically a data.frame
To use your data, you need to load it and assign it to a handle/name
Your turn: Load some data
Working with 🔗water_cleaned.xlsx
- Load the package
- Read in the Excel file and assign to object
water
Use
head()andtail()functions to look at the data
e.g.,head(water)andtail(water)Click on the
waterobject in your “Environment” pane to look at the whole data set
Your turn: Load some data
# A tibble: 6 × 6
river site element amount temperature year
<chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Grasse Up stream Al 0.606 10.9 2019
2 Grasse Mid stream Al 0.425 8.68 2020
3 Grasse Down stream Al 0.194 8.75 2021
4 Oswegatchie Up stream Al 1 0.791 2022
5 Oswegatchie Mid stream Al 0.161 9.32 2023
6 Oswegatchie Down stream Al 0.0333 10.6 2019# A tibble: 6 × 6
river site element amount temperature year
<chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Raquette Up stream Zr 0.333 14.0 2023
2 Raquette Mid stream Zr 0.111 7.61 2019
3 Raquette Down stream Zr NA 7.36 2020
4 St. Regis Up stream Zr 0.889 7.94 2021
5 St. Regis Mid stream Zr 0.778 9.28 2022
6 St. Regis Down stream Zr 0.667 10.1 2023
How do I know which function to use?
Program-specific files
- Files which only normally open in a particular program (e.g., Excel)
- Load with function from specific package (e.g.
read_excelfrom readxl package)
Text files
- Files which open in notepad
- Files which open in RStudio when you click on them in the Files Pane
- Load with function from readr package (e.g.
read_csv(),read_tsv(), etc.)
Look at the file extension:
- 🔗
water_cleaned.xlsxExcel fileread_excel() - 🔗
water_raw.csvComma-separated-variablesread_csv()
But sometimes not clear…
How do I know which function to use?
Working with: 🔗master_moch.txt
- In lower right-hand pane, click on Files
- Click on data folder
- Click on master_moch.txt
- Click “View File” (if asked)
ID region hab freq freq.sd p.notes
MCB02 kam 0.5266879074 3.9806600009 3.9806600009 0.4592592593
MCB03 kam -0.9707703735 4.1090031783 4.1090031783 0.5
MCB04 kam -0.9707703735 4.2463067674 4.2463067674 0.5151515152This does not read the file into R, but only shows you the contents as text.
Hmm, not comma-separated, maybe tab-separated?
How do I know which function to use?
Peak:
- Pick a read function with your best guess (
read_csv()is a good start) - Use
n_maxto read only first few rows
# A tibble: 3 × 1
`ID\tregion\thab\tfreq\tfreq.sd\tp.notes`
<chr>
1 "MCB02\tkam\t0.5266879074\t3.9806600009\t3.9806600009\t0.4592592593"
2 "MCB03\tkam\t-0.9707703735\t4.1090031783\t4.1090031783\t0.5"
3 "MCB04\tkam\t-0.9707703735\t4.2463067674\t4.2463067674\t0.5151515152"\t means tab, so this is tab-separated data
How do I know what to use?
Peak:
- Try again with
read_tsv()
# A tibble: 3 × 6
ID region hab freq freq.sd p.notes
<chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 MCB02 kam 0.527 3.98 3.98 0.459
2 MCB03 kam -0.971 4.11 4.11 0.5
3 MCB04 kam -0.971 4.25 4.25 0.515Excellent!
Specifics of loading functions
col_names
Working with 🔗geolocators.csv
# A tibble: 20 × 2
`02/05/11 22:29:59` `64`
<chr> <dbl>
1 02/05/11 22:31:59 64
2 02/05/11 22:33:59 38
3 02/05/11 22:35:59 38
4 02/05/11 22:37:59 34
5 02/05/11 22:39:59 30
6 02/05/11 22:41:59 34
7 02/05/11 22:43:59 40
8 02/05/11 22:45:59 46
9 02/05/11 22:47:59 48
10 02/05/11 22:49:59 46
# ℹ 10 more rowsOops?
read_csv,read_tsv, etc. assume that the first row contains the column names- This file doesn’t have headers
col_names
Working with 🔗geolocators.csv
Declare no headings
# A tibble: 21 × 2
X1 X2
<chr> <dbl>
1 02/05/11 22:29:59 64
2 02/05/11 22:31:59 64
3 02/05/11 22:33:59 38
4 02/05/11 22:35:59 38
5 02/05/11 22:37:59 34
6 02/05/11 22:39:59 30
7 02/05/11 22:41:59 34
8 02/05/11 22:43:59 40
9 02/05/11 22:45:59 46
10 02/05/11 22:47:59 48
# ℹ 11 more rowsName headings
# A tibble: 21 × 2
date light
<chr> <dbl>
1 02/05/11 22:29:59 64
2 02/05/11 22:31:59 64
3 02/05/11 22:33:59 38
4 02/05/11 22:35:59 38
5 02/05/11 22:37:59 34
6 02/05/11 22:39:59 30
7 02/05/11 22:41:59 34
8 02/05/11 22:43:59 40
9 02/05/11 22:45:59 46
10 02/05/11 22:47:59 48
# ℹ 11 more rowsskip info rows before data
Working with 🔗grain_size.txt
# A tibble: 36 × 7
`DATA DOWNLOAD: 2015-09-23` ...2 ...3 ...4 ...5 ...6 ...7
<chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr>
1 SYSTEM 001 <NA> <NA> <NA> <NA> <NA> <NA>
2 LOGGER X <NA> <NA> <NA> <NA> <NA> <NA>
3 lab_num CSP sample_num depth_lb csa msa fsa
4 3177 CSP01 CSP01-P-1-1 4 13.04 17.37 8.19
5 3178 CSP01 CSP01-P-1-2 12 10.74 16.9 7.92
6 3179 CSP01 CSP01-P-1-3 35 12.11 17.75 6.99
7 3180 CSP01 CSP01-P-1-4 53 17.61 18.16 6.29
8 3181 CSP01 CSP01-P-1-5 83 21.05 18.38 6.26
9 3182 CSP01 CSP01-P-1-6 105 19.02 18.43 6.28
10 3183 CSP08 CSP08-P-1-1 10 11.6 17.14 8.18
# ℹ 26 more rowsskip info rows before data
Working with 🔗grain_size.txt
Look at the file:
- Click on Files tab
- Click on data folder
- Click on grain_size.txt
- Click “View file” (if asked)
DATA DOWNLOAD: 2015-09-23
SYSTEM 001
LOGGER X
lab_num CSP sample_num depth_lb csa msa fsa
3177 CSP01 CSP01-P-1-1 4 13.04 17.37 8.19
3178 CSP01 CSP01-P-1-2 12 10.74 16.9 7.92
3179 CSP01 CSP01-P-1-3 35 12.11 17.75 6.99
3180 CSP01 CSP01-P-1-4 53 17.61 18.16 6.29
3181 CSP01 CSP01-P-1-5 83 21.05 18.38 6.26Ah ha!
Metadata was stored at the top of the file
skip info rows before data
Working with 🔗grain_size.txt
- Add
skip = 3to skip the first three rows
# A tibble: 33 × 7
lab_num CSP sample_num depth_lb csa msa fsa
<dbl> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 3177 CSP01 CSP01-P-1-1 4 13.0 17.4 8.19
2 3178 CSP01 CSP01-P-1-2 12 10.7 16.9 7.92
3 3179 CSP01 CSP01-P-1-3 35 12.1 17.8 6.99
4 3180 CSP01 CSP01-P-1-4 53 17.6 18.2 6.29
5 3181 CSP01 CSP01-P-1-5 83 21.0 18.4 6.26
6 3182 CSP01 CSP01-P-1-6 105 19.0 18.4 6.28
7 3183 CSP08 CSP08-P-1-1 10 11.6 17.1 8.18
8 3184 CSP08 CSP08-P-1-2 27 15.4 16.2 6.76
9 3185 CSP08 CSP08-P-1-3 90 14.9 15.8 7.12
10 3186 CSP02 CSP02-P-1-1 5 8.75 8.64 3.41
# ℹ 23 more rowsMuch better!
Your turn: Load this data set
Load Data: 🔗Sta A Data 2006-11-07.dmp
- Look at the file
- Decide which R function to use based on delimiter (comma, space, or tab?)
- Any other options need to be specified?
It should look like this:
# A tibble: 19 × 7
StartDate Time Frequency `Rate/Temp` Pwr Ant SD
<dbl> <time> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <chr> <dbl>
1 39022 17:15:36 150. 34.8 175 M0 0
2 39022 17:19:14 148. 19.2 72 M0 0
3 39022 17:19:25 148. 19.7 194 M1 0
4 39022 17:20:04 149. 33.8 104 M0 0
5 39022 17:20:17 149. 33.7 152 M1 0
6 39022 17:20:57 150. 34.2 188 M0 0
7 39022 17:22:50 148. 9.8 188 M0 0
# ℹ 12 more rowsToo Easy?
Load some of your own tricky data OR
Try to load the second sheet of water_cleaned.xlsx
Your turn: Load this data set
Load Data: 🔗Sta A Data 2006-11-07.dmp
# A tibble: 19 × 7
StartDate Time Frequency `Rate/Temp` Pwr Ant SD
<dbl> <time> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <chr> <dbl>
1 39022 17:15:36 150. 34.8 175 M0 0
2 39022 17:19:14 148. 19.2 72 M0 0
3 39022 17:19:25 148. 19.7 194 M1 0
4 39022 17:20:04 149. 33.8 104 M0 0
5 39022 17:20:17 149. 33.7 152 M1 0
6 39022 17:20:57 150. 34.2 188 M0 0
7 39022 17:22:50 148. 9.8 188 M0 0
# ℹ 12 more rowsYour turn: Load this data set
Too Easy?
- Use
sheetargument to access specific sheet (excel_sheets()lists them all) - skip the first two rows (including the headers)
[1] "Sheet1" "Oswegatchie"# A tibble: 75 × 6
river site element amount temperature year
<chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Oswegatchie Up stream Al 1 0.791 2022
2 Oswegatchie Mid stream Al 0.161 9.32 2023
3 Oswegatchie Down stream Al 0.0333 10.6 2019
4 Oswegatchie Up stream Ba 0.357 3.73 2019
5 Oswegatchie Mid stream Ba 0.560 9.66 2020
6 Oswegatchie Down stream Ba 1 8.56 2021
7 Oswegatchie Up stream Br 0.107 20.9 2021
8 Oswegatchie Mid stream Br 0.857 10.8 2022
9 Oswegatchie Down stream Br 1 4.79 2023
10 Oswegatchie Up stream Ca NA 4.76 2023
# ℹ 65 more rowsLooking for problems
Look at the data
- Make sure columns as expected (correctly assigned file format)
- Make sure no extra lines above the data (should we have used a skip?)
- Make sure column names look appropriate
# A tibble: 344 × 8
species island bill_length_mm bill_depth_mm flipper_length_mm body_mass_g sex year
<fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <int> <fct> <int>
1 Adelie Torgersen 39.1 18.7 181 3750 male 2007
2 Adelie Torgersen 39.5 17.4 186 3800 female 2007
3 Adelie Torgersen 40.3 18 195 3250 female 2007
4 Adelie Torgersen NA NA NA NA <NA> 2007
5 Adelie Torgersen 36.7 19.3 193 3450 female 2007
6 Adelie Torgersen 39.3 20.6 190 3650 male 2007
7 Adelie Torgersen 38.9 17.8 181 3625 female 2007
8 Adelie Torgersen 39.2 19.6 195 4675 male 2007
9 Adelie Torgersen 34.1 18.1 193 3475 <NA> 2007
10 Adelie Torgersen 42 20.2 190 4250 <NA> 2007
# ℹ 334 more rowsLook at the data
- Did the whole data set load?
- Are there extra blank lines at the end of the data?
# A tibble: 6 × 8
species island bill_length_mm bill_depth_mm flipper_length_mm body_mass_g sex year
<fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <int> <fct> <int>
1 Chinstrap Dream 45.7 17 195 3650 female 2009
2 Chinstrap Dream 55.8 19.8 207 4000 male 2009
3 Chinstrap Dream 43.5 18.1 202 3400 female 2009
4 Chinstrap Dream 49.6 18.2 193 3775 male 2009
5 Chinstrap Dream 50.8 19 210 4100 male 2009
6 Chinstrap Dream 50.2 18.7 198 3775 female 2009skim() the data
skim() is from skimr
- Are the formats correct?
- numbers (
numeric), - text (
character) - date (
date,POSIXct,datetime) - categories (
factor)
- numbers (
- Are values appropriate?
- Should there be
NAs?
- Should there be
- Are there any typos?
- Number of rows expected?
── Data Summary ────────────────────────
Values
Name penguins
Number of rows 344
Number of columns 8
_______________________
Column type frequency:
factor 3
numeric 5
________________________
Group variables None
── Variable type: factor ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
skim_variable n_missing complete_rate ordered n_unique top_counts
1 species 0 1 FALSE 3 Ade: 152, Gen: 124, Chi: 68
2 island 0 1 FALSE 3 Bis: 168, Dre: 124, Tor: 52
3 sex 11 0.968 FALSE 2 mal: 168, fem: 165
── Variable type: numeric ──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
skim_variable n_missing complete_rate mean sd p0 p25 p50 p75 p100 hist
1 bill_length_mm 2 0.994 43.9 5.46 32.1 39.2 44.4 48.5 59.6 ▃▇▇▆▁
2 bill_depth_mm 2 0.994 17.2 1.97 13.1 15.6 17.3 18.7 21.5 ▅▅▇▇▂
3 flipper_length_mm 2 0.994 201. 14.1 172 190 197 213 231 ▂▇▃▅▂
4 body_mass_g 2 0.994 4202. 802. 2700 3550 4050 4750 6300 ▃▇▆▃▂
5 year 0 1 2008. 0.818 2007 2007 2008 2009 2009 ▇▁▇▁▇
count() categories
count() is from dplyr*
- Check for sample sizes and potential typos in categorical columns
- Assess missing values
 * part of the
* part of the tidyverse
Plot categories
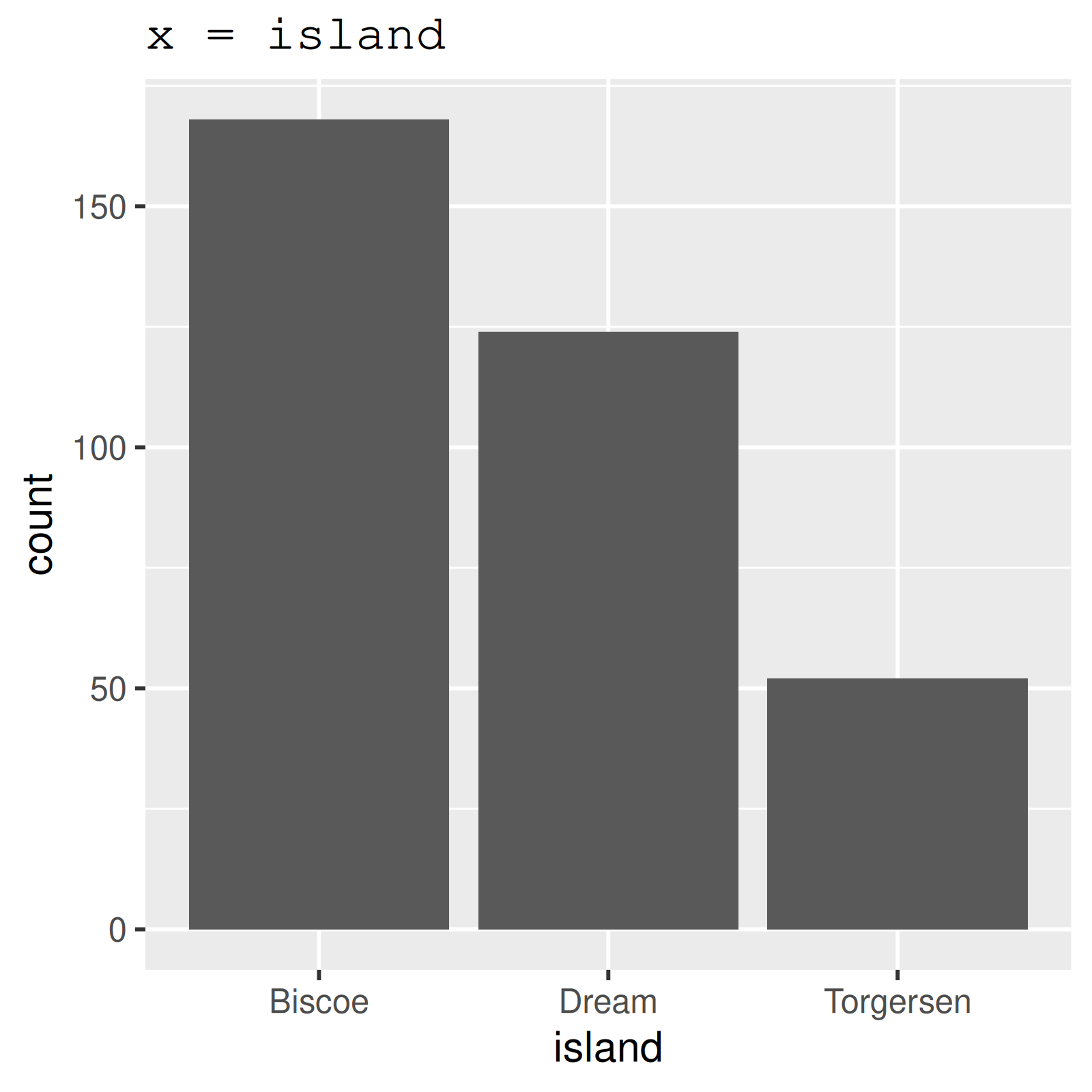
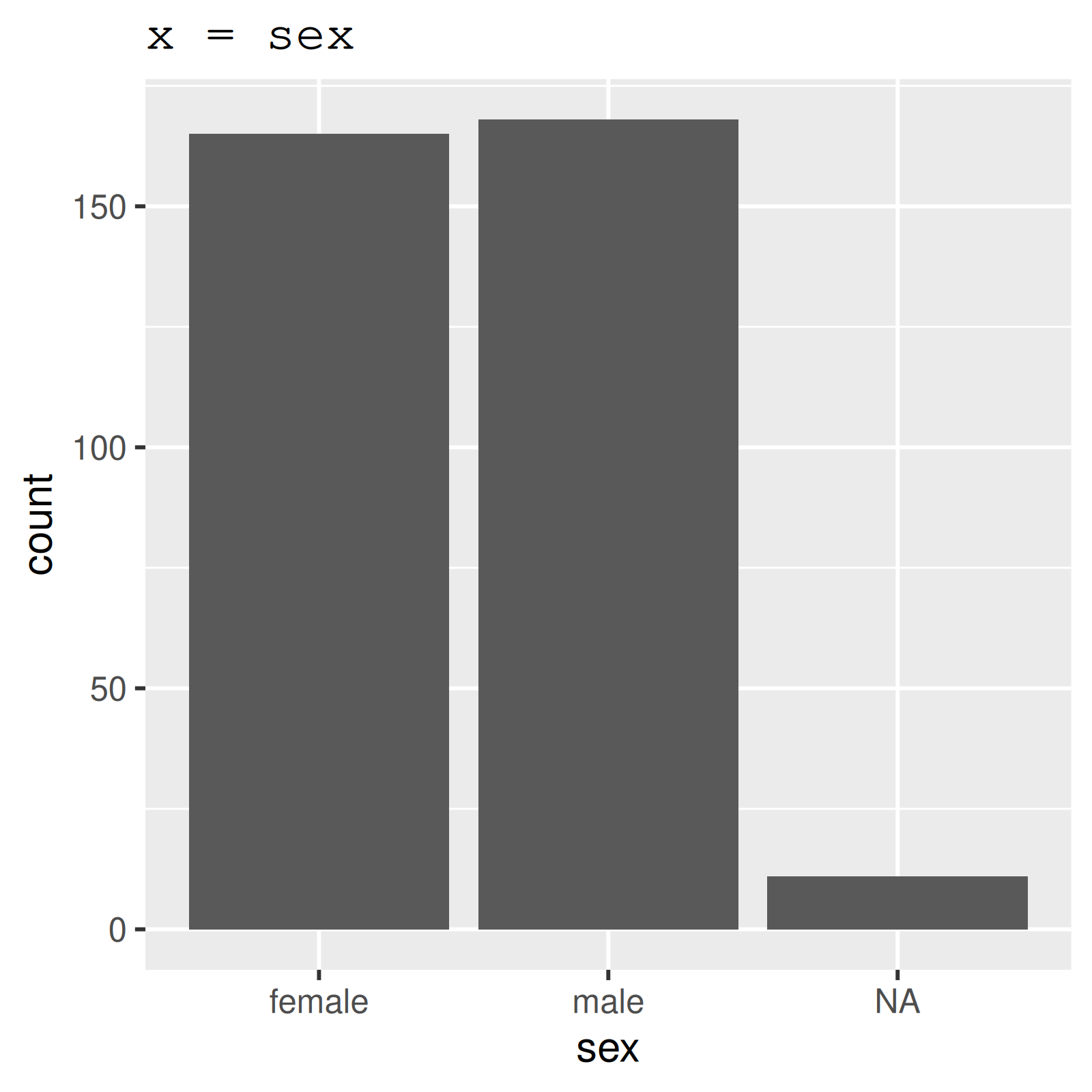
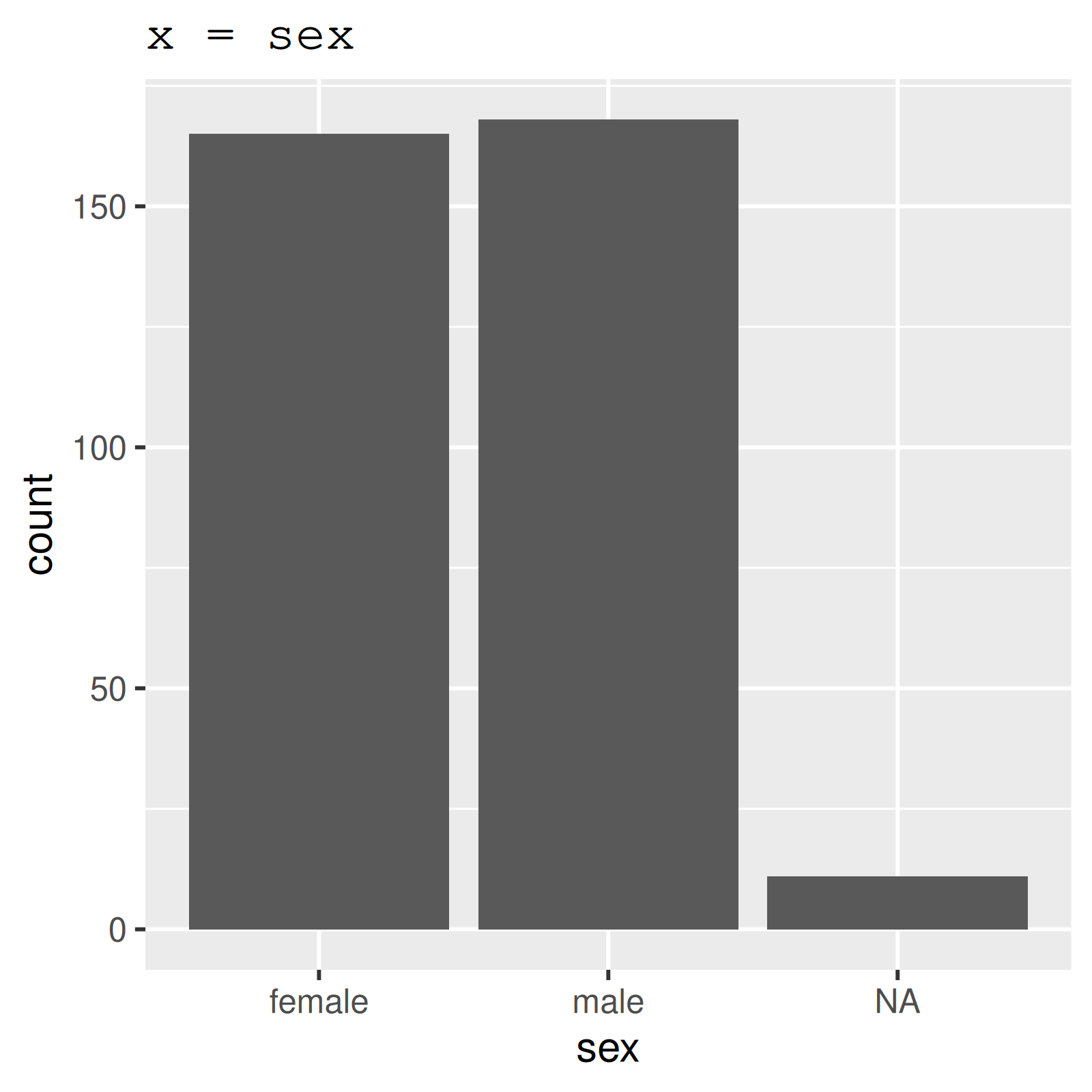
 * part of the
* part of the tidyverse
Plot numbers
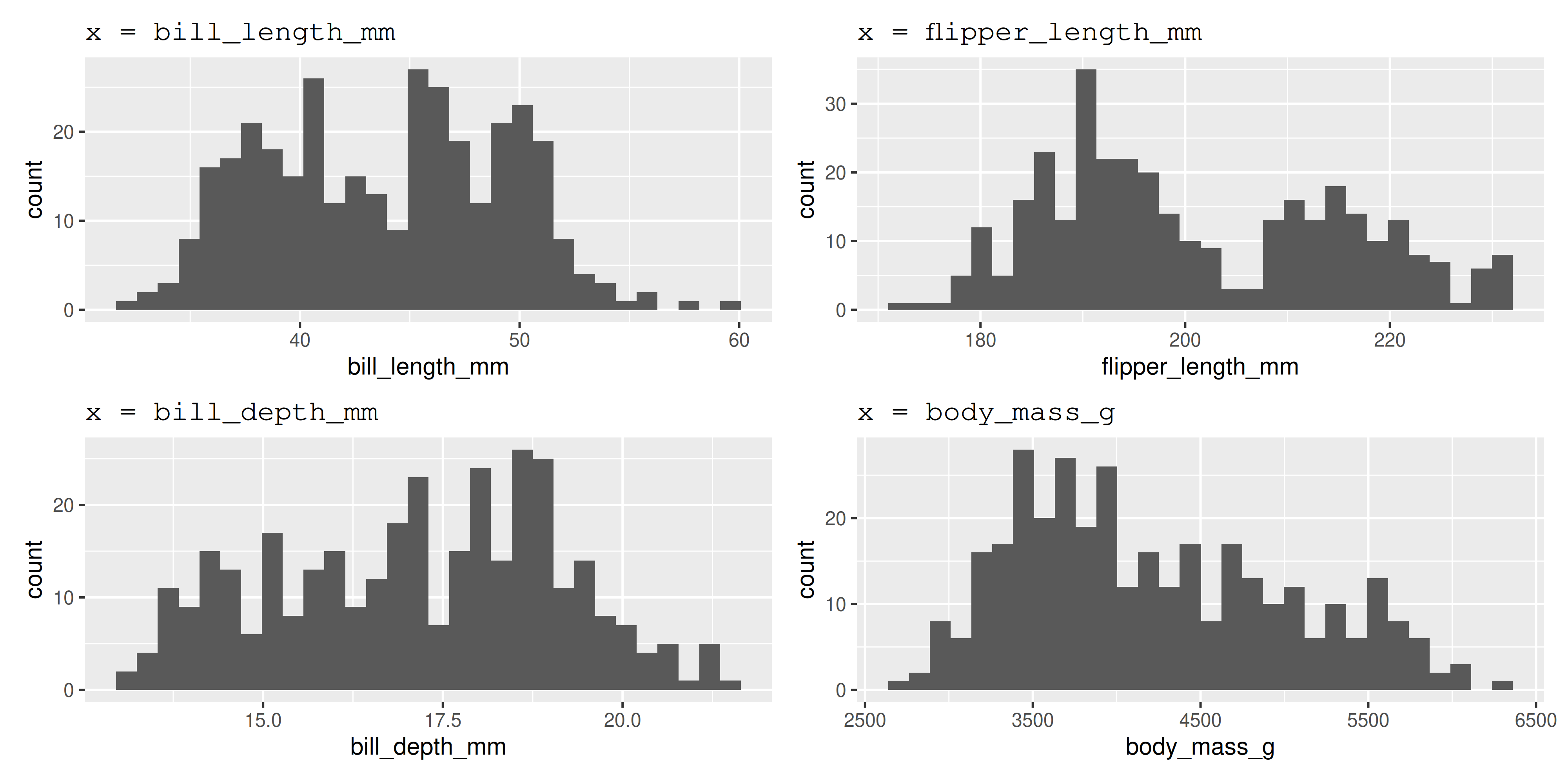
 * part of the
* part of the tidyverse
Example of problematic data
Look at the data
Working with: 🔗water_raw.csv
# A tibble: 300 × 7
`River Name` Site Ele Amo `Temperature C°` Year Wea
<chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <chr>
1 Grasse Up stream Al 0.606 10.9 2019 snowy
2 Grasse Mid stream Al 0.425 8.68 2020 cloudy
3 Grase Down stream Al 0.194 8.75 2021 cloudy
4 Oswegatchie Up stream Al 1 0.791 2022 sunny
5 Oswegatchie Mid stream Al 0.161 9.32 2023 snowy
6 Oswegatchie Down stream Al 0.0333 10.6 2019 wet
7 Raquette Up stream Al 0.292 4.01 2020 snowy
8 Raquette Mid stream Al 0.0389 5.96 2021 sunny
9 Raquette Down stream Al NA 6.21 2022 cloudy
10 St. Regis Up stream Al 0.681 8.02 2023 wet
# ℹ 290 more rows- Column names are not R-friendly (
River NameandTemperature C°) or obvious (what isEle?) - At least one typo in River (
Graseshould beGrasse)
Looking for problems
Your Turn!
# A tibble: 300 × 7
`River Name` Site Ele Amo `Temperature C°` Year Wea
<chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <chr>
1 Grasse Up stream Al 0.606 10.9 2019 snowy
2 Grasse Mid stream Al 0.425 8.68 2020 cloudy
3 Grase Down stream Al 0.194 8.75 2021 cloudy
4 Oswegatchie Up stream Al 1 0.791 2022 sunny
5 Oswegatchie Mid stream Al 0.161 9.32 2023 snowy
6 Oswegatchie Down stream Al 0.0333 10.6 2019 wet
7 Raquette Up stream Al 0.292 4.01 2020 snowy
8 Raquette Mid stream Al 0.0389 5.96 2021 sunny
9 Raquette Down stream Al NA 6.21 2022 cloudy
10 St. Regis Up stream Al 0.681 8.02 2023 wet
# ℹ 290 more rowsskim()the datacount()some columns- Perhaps make some
ggplot()s
Find any problems?
skim() the data
── Data Summary ────────────────────────
Values
Name water
Number of rows 300
Number of columns 7
_______________________
Column type frequency:
character 4
numeric 3
________________________
Group variables None
── Variable type: character ──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
skim_variable n_missing complete_rate min max empty n_unique whitespace
1 River Name 0 1 5 11 0 7 0
2 Site 0 1 9 11 0 3 0
3 Ele 0 1 1 2 0 25 0
4 Wea 0 1 3 6 0 4 0
── Variable type: numeric ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
skim_variable n_missing complete_rate mean sd p0 p25 p50 p75 p100 hist
1 Amo 39 0.87 0.429 0.299 0.00656 0.169 0.379 0.643 1 ▇▆▆▃▃
2 Temperature C° 0 1 9.17 11.5 -99 7.54 10.3 12.7 20.9 ▁▁▁▁▇
3 Year 0 1 2021 1.42 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 ▇▇▇▇▇count() categories
Plot categories
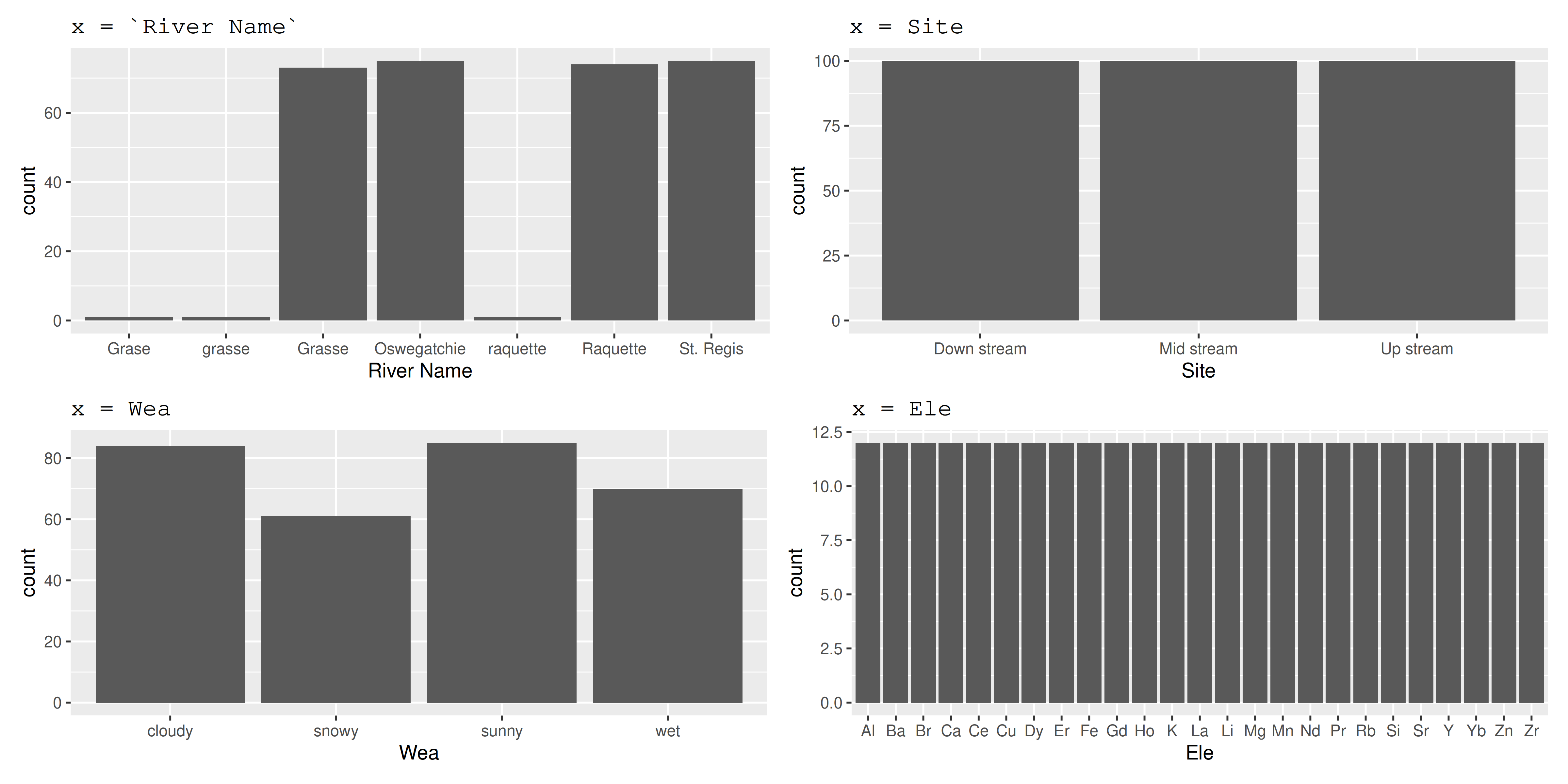
Plot numbers
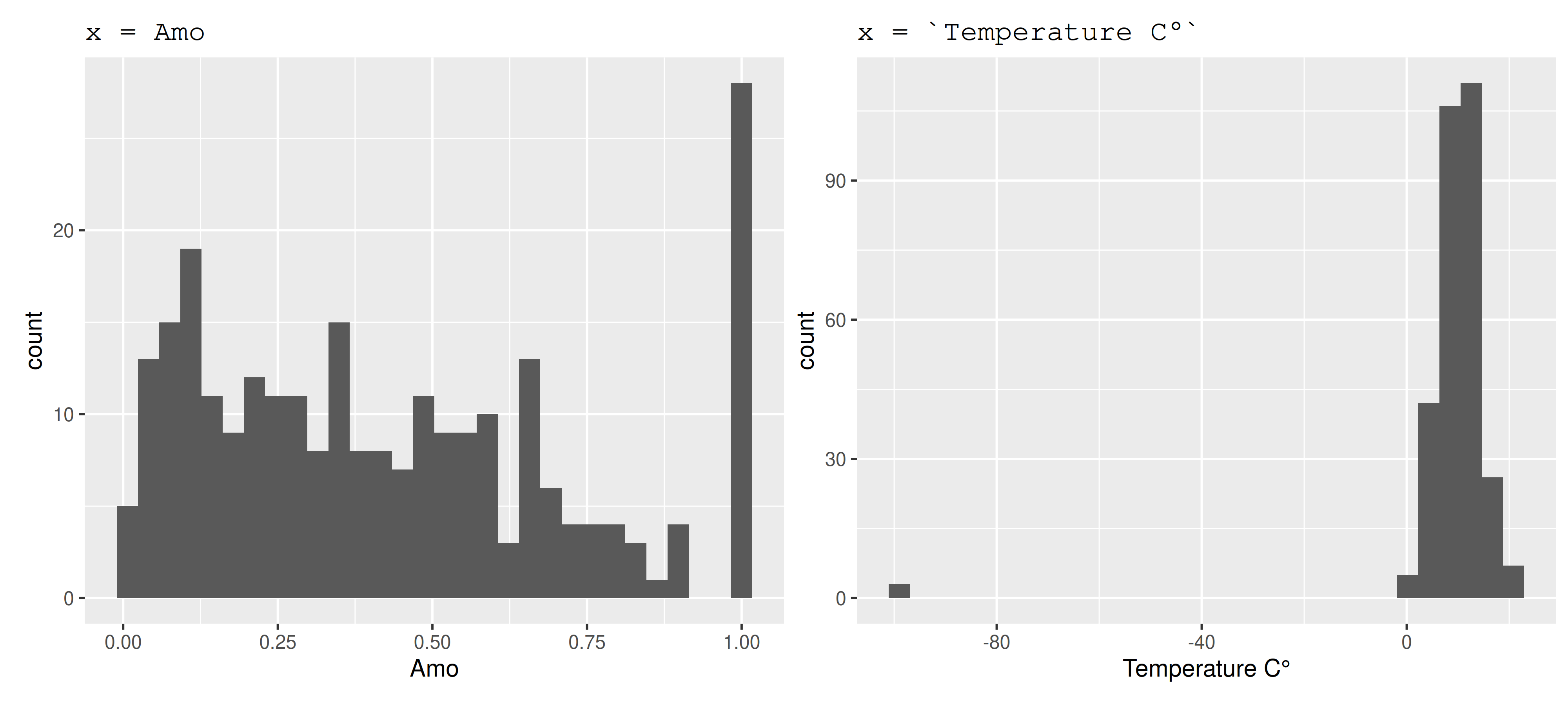
Fixing problems
Cleaning column names
clean_names() is from janitor*
* not part of the tidyverse but tidyverse-orientated
# A tibble: 300 × 7
river_name site ele amo temperature_c year wea
<chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <chr>
1 Grasse Up stream Al 0.606 10.9 2019 snowy
2 Grasse Mid stream Al 0.425 8.68 2020 cloudy
3 Grase Down stream Al 0.194 8.75 2021 cloudy
4 Oswegatchie Up stream Al 1 0.791 2022 sunny
5 Oswegatchie Mid stream Al 0.161 9.32 2023 snowy
6 Oswegatchie Down stream Al 0.0333 10.6 2019 wet
7 Raquette Up stream Al 0.292 4.01 2020 snowy
8 Raquette Mid stream Al 0.0389 5.96 2021 sunny
9 Raquette Down stream Al NA 6.21 2022 cloudy
10 St. Regis Up stream Al 0.681 8.02 2023 wet
# ℹ 290 more rows
Side Note: Naming conventions

Side Note: Naming conventions
Cleaning column names
rename() is from dplyr*
rename() columns
# A tibble: 300 × 7
river_name site element amount temperature year wea
<chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <chr>
1 Grasse Up stream Al 0.606 10.9 2019 snowy
2 Grasse Mid stream Al 0.425 8.68 2020 cloudy
3 Grase Down stream Al 0.194 8.75 2021 cloudy
4 Oswegatchie Up stream Al 1 0.791 2022 sunny
5 Oswegatchie Mid stream Al 0.161 9.32 2023 snowy
6 Oswegatchie Down stream Al 0.0333 10.6 2019 wet
7 Raquette Up stream Al 0.292 4.01 2020 snowy
8 Raquette Mid stream Al 0.0389 5.96 2021 sunny
9 Raquette Down stream Al NA 6.21 2022 cloudy
10 St. Regis Up stream Al 0.681 8.02 2023 wet
# ℹ 290 more rows * part of the
* part of the tidyverse
Subsetting columns
select() is from dplyr*
select() columns you want
 * part of the
* part of the tidyverse
OR, unselect() columns you don’t want
# A tibble: 300 × 6
river_name site element amount temperature year
<chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Grasse Up stream Al 0.606 10.9 2019
2 Grasse Mid stream Al 0.425 8.68 2020
3 Grase Down stream Al 0.194 8.75 2021
4 Oswegatchie Up stream Al 1 0.791 2022
5 Oswegatchie Mid stream Al 0.161 9.32 2023
6 Oswegatchie Down stream Al 0.0333 10.6 2019
7 Raquette Up stream Al 0.292 4.01 2020
8 Raquette Mid stream Al 0.0389 5.96 2021
9 Raquette Down stream Al NA 6.21 2022
10 St. Regis Up stream Al 0.681 8.02 2023
# ℹ 290 more rowsCleaning columns
Put it all together
water <- read_csv("data/water_raw.csv")
water <- clean_names(water)
water <- rename(water, element = ele, amount = amo, temperature = temperature_c)
water <- select(water, -wea)
water# A tibble: 300 × 6
river_name site element amount temperature year
<chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Grasse Up stream Al 0.606 10.9 2019
2 Grasse Mid stream Al 0.425 8.68 2020
3 Grase Down stream Al 0.194 8.75 2021
4 Oswegatchie Up stream Al 1 0.791 2022
5 Oswegatchie Mid stream Al 0.161 9.32 2023
6 Oswegatchie Down stream Al 0.0333 10.6 2019
7 Raquette Up stream Al 0.292 4.01 2020
8 Raquette Mid stream Al 0.0389 5.96 2021
9 Raquette Down stream Al NA 6.21 2022
10 St. Regis Up stream Al 0.681 8.02 2023
# ℹ 290 more rowsNote how code repeats data frame water…
Fixing typos
Remember the typos…
Fixing typos
Replace typos
Combine the if_else function with the mutate() function
Check that it’s gone:
Fixing typos
if_else() and mutate() from dplyr package*
if_else() tests for a condition, and returns one value if FALSE and another if TRUE
 * part of the
* part of the tidyverse
Iterative process
- Make some corrections
- Check the data
- Make some more corrections (either add to or modify existing code)
Your Turn: Fix another “Grasse” typo
- Check the data with
count() - Use
mutate()andif_else()to fix the typo
Too Easy?
Examine and fix problems in your own data OR
Use case_when() to fix all the river name typos at once…
Your Turn: Fix another “Grasse” typo
- Check the data with
count() - Use
mutate()andif_else()to fix the typo
water <- read_csv("data/water_raw.csv")
water <- clean_names(water)
water <- rename(water, element = ele, amount = amo, temperature = temperature_c)
water <- select(water, -wea)
water <- mutate(water, river_name = if_else(river_name == "Grase", "Grasse", river_name))
water <- mutate(water, river_name = if_else(river_name == "grasse", "Grasse", river_name))Fixing typos
To be more efficient, fix all typos at once
== compares one item to one other%in% compares one item to many different ones
Fixing typos
One last typo to fix
water <- read_csv("data/water_raw.csv")
water <- clean_names(water)
water <- rename(water, element = ele, amount = amo, temperature = temperature_c)
water <- select(water, -wea)
water <- mutate(water,
river_name = if_else(river_name %in% c("Grase","grasse"), "Grasse", river_name),
river_name = if_else(river_name == "raquette", "Raquette", river_name))Combine with case_when()
water <- read_csv("data/water_raw.csv")
water <- clean_names(water)
water <- rename(water, element = ele, amount = amo, temperature = temperature_c)
water <- select(water, -wea)
water <- mutate(water,
river_name = case_when(river_name %in% c("Grase", "grasse") ~ "Grasse",
river_name == "raquette" ~ "Raquette",
TRUE ~ river_name))Tangent: tidyverse functions
tidyverse functions
rename(), select(), mutate()
tidyversefunctions always start with the data, followed by other arguments- you can reference any column from ‘data’
rename()changes column namesselect()chooses columns to keep or to remove (with-)mutate()changes column contents

Why use tidyverse functions?
Pipes! |>* Allow you to string commands together
Instead of:
water <- read_csv("data/water_raw.csv")
water <- clean_names(water)
water <- rename(water, element = ele, amount = amo, temperature = temperature_c)
water <- select(water, -wea)
water <- mutate(water,
river_name = case_when(river_name %in% c("Grase", "grasse") ~ "Grasse",
river_name == "raquette" ~ "Raquette",
TRUE ~ river_name))* |> is the base pipe, %>% is the tidyverse pipe, you can use either

Play around
Take a moment to play with this code in your console
Convert this:
water <- read_csv("data/water_raw.csv")
water <- clean_names(water)
water <- rename(water, element = ele, amount = amo, temperature = temperature_c)
water <- select(water, -wea)
water <- mutate(water,
river_name = case_when(river_name %in% c("Grase", "grasse") ~ "Grasse",
river_name == "raquette" ~ "Raquette",
TRUE ~ river_name))To this:

Dealing with NAs
Data that is missing
Data that should be missing
Exploring NAs
- We saw missing values in
amount - Use
filter()to take a closer look
# A tibble: 39 × 6
river_name site element amount temperature year
<chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Raquette Down stream Al NA 6.21 2022
2 Raquette Up stream Ba NA 5.23 2022
3 Raquette Up stream Br NA -99 2019
4 Oswegatchie Up stream Ca NA 4.76 2023
5 Raquette Down stream Ce NA 13.9 2020
6 Grasse Up stream Cu NA 9.13 2019
7 Raquette Down stream Dy NA 4.98 2019
8 Raquette Down stream Er NA 3.07 2021
9 Raquette Down stream Fe NA 7.20 2023
10 Raquette Down stream Gd NA 4.73 2020
# ℹ 29 more rowsOmitting NAs
drop_na() is from tidyr*
Omit NAs from the amount column only (drop those rows)
Omit all NAs from all columns (drop those rows)
Check…
# A tibble: 0 × 6
# ℹ 6 variables: river_name <chr>, site <chr>, element <chr>, amount <dbl>, temperature <dbl>, year <dbl>[1] 261No more NAs!
Fewer rows
* part of the tidyverse 
Side Note: filter() also omits NAs 😱
If we filter by the column with NAs, they are silently dropped
# A tibble: 15 × 6
river_name site element amount temperature year
<chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Oswegatchie Down stream Al 0.0333 10.6 2019
2 Raquette Mid stream Al 0.0389 5.96 2021
3 Grasse Mid stream Br 0.0357 12.4 2019
4 St. Regis Up stream Br 0.0357 3.52 2022
5 St. Regis Mid stream Br 0.0357 0.936 2023
6 Raquette Mid stream Ce 0.0116 6.61 2019
7 Raquette Mid stream Fe 0.00656 10.8 2022
8 Grasse Up stream K 0.0313 3.61 2021
9 Raquette Mid stream La 0.0275 2.50 2020
10 Oswegatchie Down stream Mn 0.00672 8.89 2019
# ℹ 5 more rowsWe need to be explicit if we want to keep them
# A tibble: 54 × 6
river_name site element amount temperature year
<chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Oswegatchie Down stream Al 0.0333 10.6 2019
2 Raquette Mid stream Al 0.0389 5.96 2021
3 Raquette Down stream Al NA 6.21 2022
4 Raquette Up stream Ba NA 5.23 2022
5 Grasse Mid stream Br 0.0357 12.4 2019
6 Raquette Up stream Br NA -99 2019
7 St. Regis Up stream Br 0.0357 3.52 2022
8 St. Regis Mid stream Br 0.0357 0.936 2023
9 Oswegatchie Up stream Ca NA 4.76 2023
10 Raquette Mid stream Ce 0.0116 6.61 2019
# ℹ 44 more rowsReplacing NAs
replace_na() is from tidyr*
Check…
# A tibble: 0 × 6
# ℹ 6 variables: river_name <chr>, site <chr>, element <chr>, amount <dbl>, temperature <dbl>, year <dbl>[1] 300No more NAs!
Same number of rows
(If you want to do a more complex replacement, you’ll have to use if_else() or case_when() like we did for typos.)
* part of the tidyverse 
Converting to NA
Remember the problem with temperature?
# A tibble: 3 × 6
river_name site element amount temperature year
<chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Raquette Up stream Br NA -99 2019
2 Oswegatchie Mid stream K 0.426 -99 2020
3 St. Regis Mid stream La 0.367 -99 2023na_if() is from dplyr*
 * part of the
* part of the tidyverse
Fixing formats
Fixing formats
Basic data types
- Text (Characters or Strings)
- Numbers (Doubles, Integers)
- Logical (TRUE or FALSE)
- Factor (Categories)
- Dates
- Date/Times
Look for problems
# A tibble: 300 × 6
river_name site element amount temperature year
<chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Grasse Up stream Al 0.606 10.9 2019
2 Grasse Mid stream Al 0.425 8.68 2020
3 Grasse Down stream Al 0.194 8.75 2021
4 Oswegatchie Up stream Al 1 0.791 2022
5 Oswegatchie Mid stream Al 0.161 9.32 2023
6 Oswegatchie Down stream Al 0.0333 10.6 2019
7 Raquette Up stream Al 0.292 4.01 2020
8 Raquette Mid stream Al 0.0389 5.96 2021
9 Raquette Down stream Al NA 6.21 2022
10 St. Regis Up stream Al 0.681 8.02 2023
# ℹ 290 more rowsYear could be categorical (factor)
Better for plotting!
(although it really depends)
Convert to categorical
# A tibble: 300 × 6
river_name site element amount temperature year
<chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <fct>
1 Grasse Up stream Al 0.606 10.9 2019
2 Grasse Mid stream Al 0.425 8.68 2020
3 Grasse Down stream Al 0.194 8.75 2021
4 Oswegatchie Up stream Al 1 0.791 2022
5 Oswegatchie Mid stream Al 0.161 9.32 2023
6 Oswegatchie Down stream Al 0.0333 10.6 2019
7 Raquette Up stream Al 0.292 4.01 2020
8 Raquette Mid stream Al 0.0389 5.96 2021
9 Raquette Down stream Al NA 6.21 2022
10 St. Regis Up stream Al 0.681 8.02 2023
# ℹ 290 more rowsChanging classes
| Function | Input | Output |
|---|---|---|
as.character() |
Any vector | Text (Characters) |
as.numeric() |
Any vector (but returns NAs if not numbers) | Numbers |
as.logical() |
TRUE, FALSE, T, F, 1, 0 (FALSE), any other number (all TRUE) | TRUE or FALSE |
as.factor() |
Any vector | Categories |
We’ll deal with dates and times later…
Put it all together…
water <- read_csv("data/water_raw.csv") |>
clean_names() |>
rename(element = ele, amount = amo, temperature = temperature_c) |>
select(-wea) |>
mutate(river_name = case_when(river_name %in% c("Grase", "grasse") ~ "Grasse",
river_name == "raquette" ~ "Raquette",
TRUE ~ river_name),
amount = replace_na(amount, 0),
temperature = na_if(temperature, -99),
year = as.factor(year)) And you have a clean, corrected data frame ready to use
- You have not changed the original data
- You have a reproducible record of all corrections
- You can alter these corrections at any time
- You have formatted your data for use in R
- Read these steps line by line to remind yourself what you did
Put it all together…
Feel free to annotate within a pipe
water <- read_csv("data/water_raw.csv") |>
# Fix column names
clean_names() |>
rename(element = ele, amount = amo, temperature = temperature_c) |>
select(-wea) |>
mutate(
# Correct typos
river_name = case_when(river_name %in% c("Grase", "grasse") ~ "Grasse",
river_name == "raquette" ~ "Raquette",
TRUE ~ river_name),
# Missing amounts should be 0
amount = replace_na(amount, 0),
# Problems with temperature logger, -99 is a mistake
temperature = na_if(temperature, -99),
# Convert for plotting
year = as.factor(year)) Dates and Times
(Or why does R hate me?)
Dates and Times
Working with 🔗geolocators.csv
- Date/times aren’t always recognized as date/times
# A tibble: 21 × 2
time light
<chr> <dbl>
1 02/05/11 22:29:59 64
2 02/05/11 22:31:59 64
3 02/05/11 22:33:59 38
4 02/05/11 22:35:59 38
5 02/05/11 22:37:59 34
6 02/05/11 22:39:59 30
# ℹ 15 more rowsHere
timecolumn is consideredchr(character/text)You may know it’s a date, but R does not
Artwork by @allison_horst
lubridate package*
- Part of
tidyverse, but needs to be loaded separately - Great for converting date/times (i.e. telling R this is a date/time)
# A tibble: 21 × 3
time light time_fixed
<chr> <dbl> <dttm>
1 02/05/11 22:29:59 64 2011-05-02 22:29:59
2 02/05/11 22:31:59 64 2011-05-02 22:31:59
3 02/05/11 22:33:59 38 2011-05-02 22:33:59
4 02/05/11 22:35:59 38 2011-05-02 22:35:59
5 02/05/11 22:37:59 34 2011-05-02 22:37:59
6 02/05/11 22:39:59 30 2011-05-02 22:39:59
# ℹ 15 more rowsNow
time_fixedcolumn is considereddttm(Date/Time)So You know it’s a Date/Time and now R knows too
 * part of the
* part of the tidyverse
lubridate package*

Generally, only the order of the year, month, day, hour, minute, or second matters.
For example
| date/time format | function | output class |
|---|---|---|
| 2018-01-01 13:09:11 | ymd_hms() |
dttm (POSIXct/POSIXt) |
| 12/20/2019 10:00 PM | mdy_hm() |
dttm (POSIXct/POSIXt) |
| 31/01/2000 10 AM | dmy_h() |
dttm (POSIXct/POSIXt) |
| 31-01/2000 | dmy() |
Date |
lubridateis smart enough to detect AMs and PMs
Note: R generally requires that times have dates (datetime/POSIXct), but dates don’t have to have times (Date)
* part of the tidyverse
Saving data
For the love of all that is good don’t lose that data!!!*
* but if you’ve been paying attention, you know that you only need the script 😉
Saving data
Keep yourself organized
- Keep your R-created data in a different folder from your ‘raw’ data*
- If you have a lot going on, split your work into several scripts, and number the both the scripts AND the data sets produced:
1_cleaned.csv2_summarized.csv3_graphing.csv
Save your data to file:
- First create the datasets folder

* I usually have a data folder and then both raw and datasets folders inside of that
Dealing with data
1. Loading data
- Get your data into R
2. Looking for problems
- Typos
- Incorrectly loaded data
3. Fixing problems
- Corrections
- Renaming
- Dealing with NA’s
4. Setting formats
- Text
- Numbers
- Factors
- Dates
5. Saving your data
Wrapping up: Common mistakes
Assuming your data is in one format when it’s not
- Print your data to the console and use
skim()to explore the format of your data - Use
skim(),count(),filter(),select(),ggplot()to explore the content of your data
Wrapping up: Common mistakes
Confusing pipes with function arguments
- Pipes (
|>or%>%) pass the output from one function as input (first argument) to the next function
- Arguments may be on different lines, but all part of one function